The Real Truth About Omega Fats: Breaking Down the Hype, Science, and What Your Body Actually Needs

We’re living through what some call The Great Noticing—a collective awakening to what we’ve been fed, sold, and taught to ignore. Now more than ever, people are waking up to the role that nutrition plays in health, healing, and chronic disease. Among the most misunderstood topics? Omega fatty acids. This omega fatty acids guide will give you the full breakdown on what they are, why they matter, and how to balance them.
Let’s set the record straight.
🧠 What Are Omega Fatty Acids?
Omega fatty acids are unsaturated fats critical for everything from cell membranes and hormone production to brain health and inflammation control. The main types that impact your health are:
- Omega-3 (ALA, EPA, DHA)
- Omega-6 (LA, GLA)
- Omega-7 (Palmitoleic Acid)
- Omega-9 (Oleic Acid)
This omega fatty acids guide will help you understand that not all omegas are created equal—and balance is everything.
🧠 Omega-3 Fatty Acids: The Anti-Inflammatory Fat That’s Been Silently Saving Lives
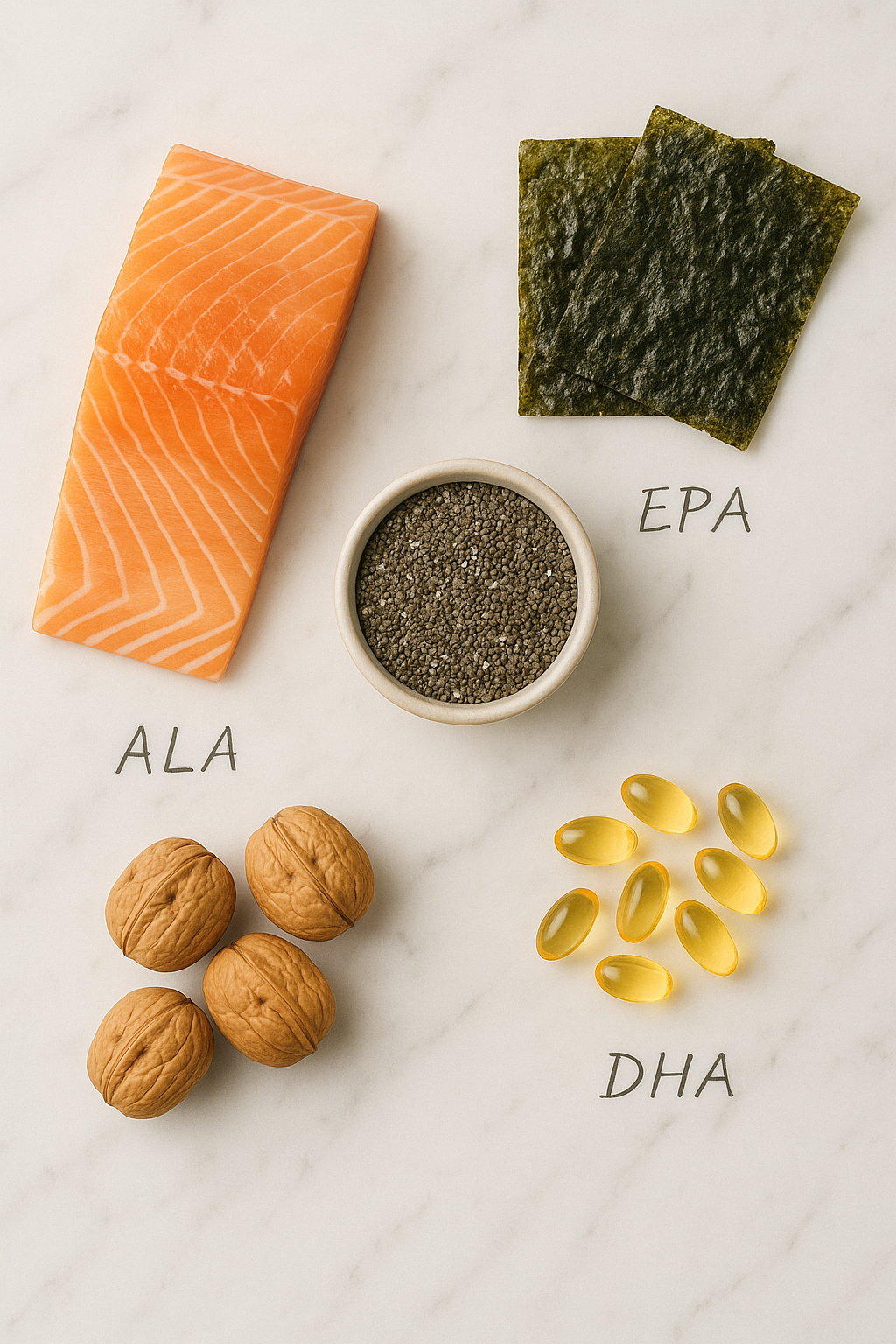

Omega-3s are essential fats your body can’t make. That means you either eat them or live without them — and going without has a cost: inflammation, brain fog, accelerated aging, and higher cancer risk.
The Big Three:
- ALA: Flax, chia, hemp, walnuts
- EPA & DHA: Fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, sardines
Benefits:
- Reduces inflammation and supports heart health
- Enhances brain function and memory
- Supports mental health and hormonal balance
- Shown in studies to reduce cancer progression and mortality (Mayo Clinic Study, DO-HEALTH Trial)
Caution:
- Mega-doses can cause GI upset, atrial fibrillation, or increase LDL in some people
- Quality and dosage matter—food first, supplements second
⚖️ Omega-6 Fatty Acids: Vital, Misunderstood, and Often Overshadowed
 You need omega-6 fatty acids—especially linoleic acid (LA)—for immune function, skin health, and cellular integrity. But in excess, especially when omega-3 intake is low, omega-6s can contribute to inflammation and chronic disease.
You need omega-6 fatty acids—especially linoleic acid (LA)—for immune function, skin health, and cellular integrity. But in excess, especially when omega-3 intake is low, omega-6s can contribute to inflammation and chronic disease.
Main Sources:
- LA: Vegetable oils (soybean, corn, sunflower)
- GLA: Borage oil, evening primrose oil
Benefits:
- Improves lipid metabolism
- Supports skin health and hormone balance
- Some forms (GLA) are anti-inflammatory (GLA Clinical Study)

Risks:
- Overconsumption from processed foods distorts omega-6/omega-3 ratio (modern diets can reach 20:1)
- Isolated studies show possible tumor growth acceleration in aggressive breast cancers (Study Link)
Key Point: Omega-6 isn’t the enemy—imbalance is.
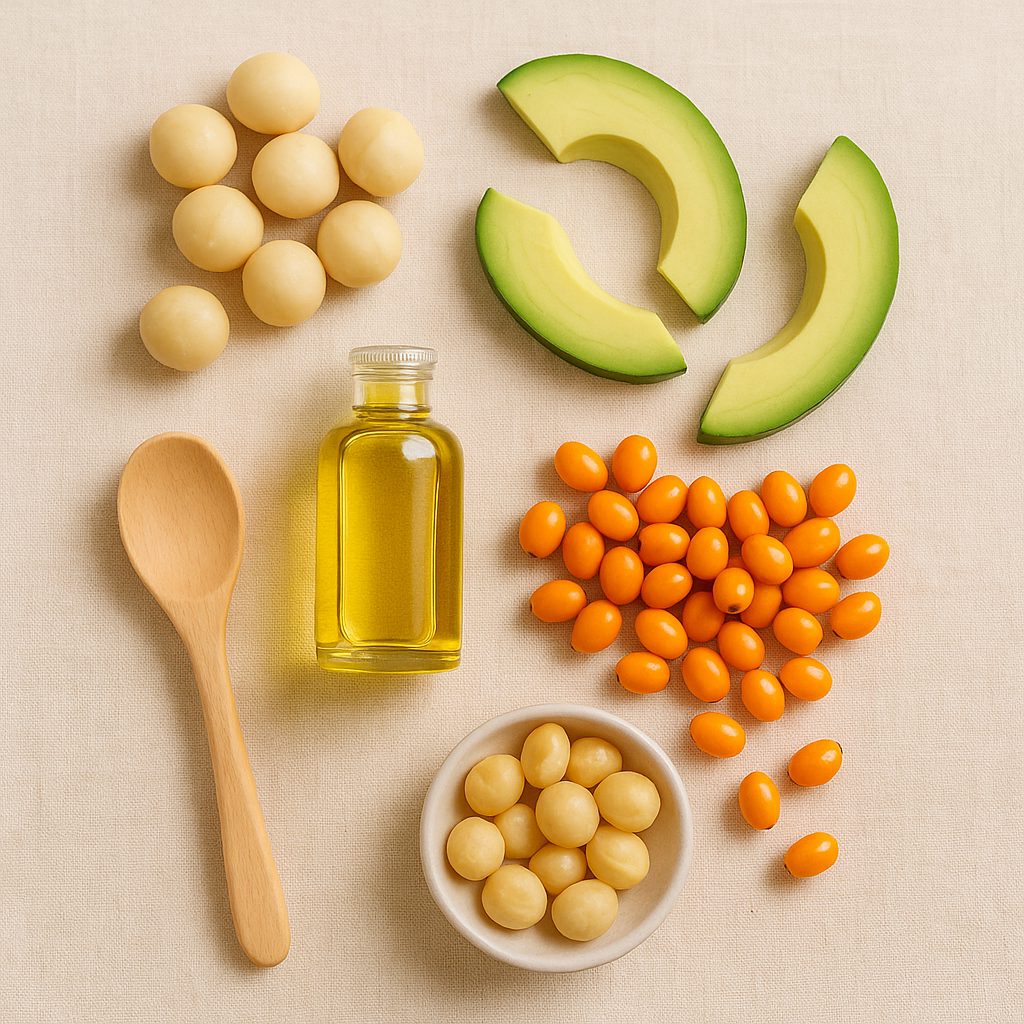
✨ Omega-7 Fatty Acids: The Skin, Gut & Metabolism Whisperer
Omega-7 isn’t essential, but it’s emerging as a valuable ally. Found in macadamia nuts and sea buckthorn oil, palmitoleic acid supports mucosal healing, insulin sensitivity, and collagen production.
Sources:
- Macadamia nuts, sea buckthorn berries, avocados, full-fat dairy
Benefits:
- Improves skin elasticity and barrier function
- May reduce CRP (inflammatory marker)
- Supports gut lining repair
Limitations:
- Human studies are mixed; one trial showed no significant benefits over placebo
- Overhyped in supplements without strong clinical backing
Use omega-7 like a whisper, not a megaphone—subtle but powerful.
🫒 Omega-9 Fatty Acids: The Heart & Mood Ally You Can Make, But Shouldn’t Ignore
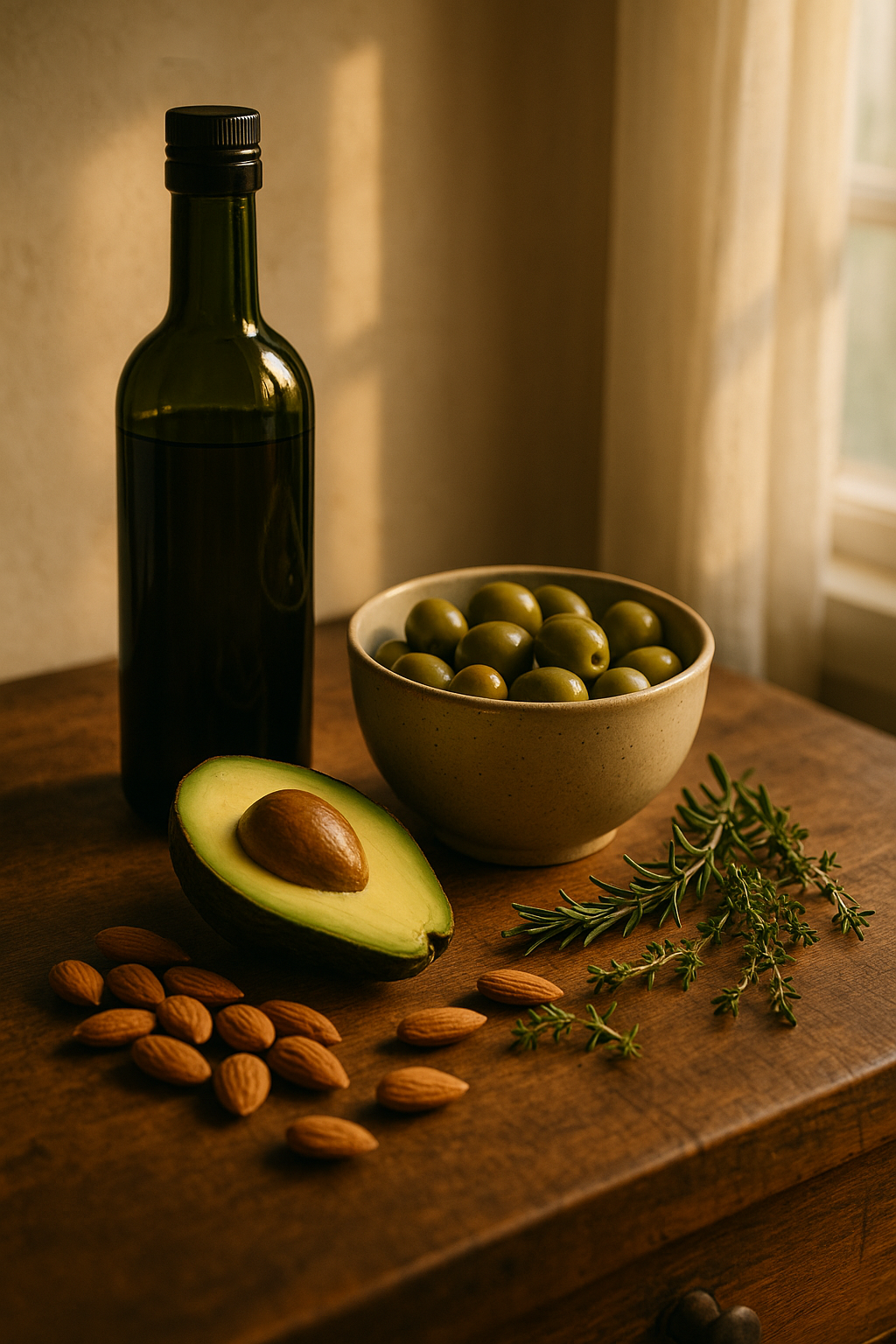

Your body can make omega-9 (oleic acid), but dietary sources like olive oil and avocados supercharge its benefits.
Sources:
- Olive oil, avocado, almonds, macadamia oil
Benefits:
- Lowers LDL and raises HDL cholesterol
- Activates PPAR pathways that reduce inflammation
- Linked to improved mood and energy levels (Mood Study via Dr. Axe)
Cautions:
- High caloric density: quality over quantity
- Some mouse models suggest excess may promote fat-cell formation
Best Used:
- As a replacement, not an addition. Drizzle, don’t drown.
📊 Omega Fatty Acids Comparison Table
| Omega Type | Main Fats | Sources | Benefits | Risks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Omega-3 | ALA, EPA, DHA | Fish, flax, chia | Anti-inflammatory, brain & heart health, longevity | Excess supplement use can trigger side effects |
| Omega-6 | LA, GLA | Seed oils, borage, primrose | Skin, hormone, immune, metabolism | Inflammation if unbalanced; cancer link in isolated studies |
| Omega-7 | Palmitoleic acid | Macadamia, sea buckthorn | Gut, skin, insulin regulation | Evidence weak; don’t over-supplement |
| Omega-9 | Oleic acid | Olive, avocado, nuts | Heart, brain, mood, inflammation | Can promote weight gain if overused |
⚖️ Practical Tips to Balance Your Omega Fatty Acids
- 🌿 Prioritize Omega-3s: Eat wild fatty fish, flaxseed, and pastured eggs regularly.
- ❌ Limit Industrial Omega-6: Avoid ultra-processed snacks and high-heat seed oils.
- ↺ Rotate Your Fats: Olive for salads, avocado for sautéing, macadamia in baking.
- ⚖️ Focus on Ratio, Not Elimination: Use food-based fats to find your body’s natural balance.
- 📈 Supplement Wisely: Choose clean fish oil if needed, and avoid mega-doses.
🔄 Final Thoughts: Balance Is Biologic
Your body was built for balance—not excess, not avoidance. Omega fats aren’t enemies or heroes. They’re messengers, builders, and healers when used in harmony. This omega fatty acids guide shows you how to reclaim that harmony with real food and intentional choices.
So don’t chase the trend. Reclaim the rhythm. Balance your fats, and you just might balance your life.